

Illustrated Encyclopedia of Human Anatomic Variation: Opus III: Nervous System
Ronald A. Bergman, PhD
Adel K. Afifi, MD, MS
Ryosuke Miyauchi, MD
Peer Review Status: Internally Peer Reviewed
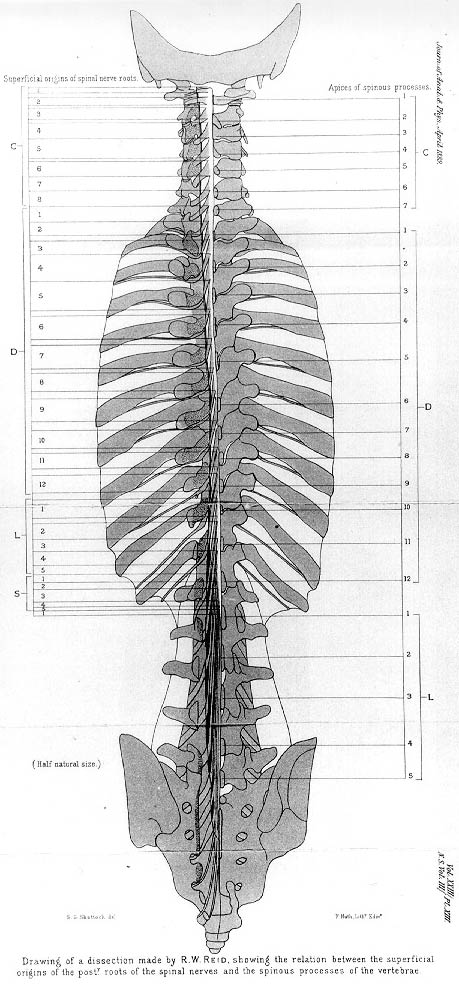
A: Drawing of a dissection made by R.W. Reid showing the relation between the superficial origins of the posterior roots of the spinal nerves and the spinous processes of the vertebrae. C, cervical; D (dorsal), thoracic; L, lumbar; S, sacral vertebrae.
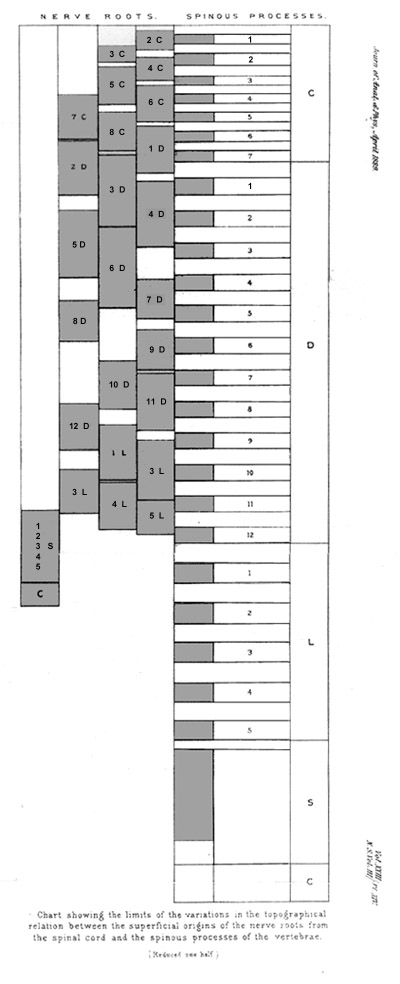
B: Chart showing the limits of the variations in the topographical relation between the superficial origins of the nerve roots from the spinal cord and the spinous processes of the vertebrae. Abbreviations as in drawing A.
The following summary may therefore be made of the limits within which Reid found the posterior and anterior nerve roots take their superficial origin from the cord, in relation to the posterior ends of the spinous processes in the six specimens examined. (A signifies the highest point of origin; B, the lowest point of origin.)
Nerves
2nd Cervical: A, A little above posterior arch of atlas; B, midway between posterior arch of atlas and spine of axis.
3rd Cervical: A, A little below posterior arch of atlas; B, junction of upper 2/3 and lower 1/3 of spine of axis.
4th Cervical: A, Just below upper border of spine of axis; B. middle of spine of C3.
5th Cervical: A, Just below lower border of spine of axis; B, just below lower border of spine Of C4
6th Cervical: A, Lower border of spine of C3; B, lower border of spine of C5.
7th Cervical: A, Just below upper border of spine Of C4; B, just above lower border of spine of C6.
8th Cervical: A, Upper border of spine of C5; B, upper border of spine of C7
1st Dorsal: A, Midway between spines of C5 and C6; B, junction of upper 2/3 and lower 1/3 of interval between C7 and D1.
2nd Dorsal: A, Lower border of spine of C6; B, just above lower border of spine of D1
3rd Dorsal: A, Just above middle of spine Of C7; B, lower border of spine of D2.
4th Dorsal: A, Just below upper border of spine of D1; B, junction of upper 1/3 and lower 2/3 of spine of D3
5th Dorsal: A, Upper border of spine of D2; B, junction of upper 1/4 and lower 3/4 of spine of D4.
6th Dorsal: A, Lower border of spine of D2; B, just below upper border of spine of D5.
7th Dorsal: A, Junction of upper 1/3 and lower 2/3 of spine of D4; B just above lower border of spine of D5.
8th Dorsal: A, Junction of upper 2/3 and lower 1/3 of interval between spines of D4 and D5; B, junction of upper 1/4 and lower 3/4 of spine of D6.
9th Dorsal: A, Midway between spines of D5 and D6; B, upper border of spine of D7.
10th Dorsal: A, Midway between spines of D6, and D7; B, middle of spine of D8.
11th Dorsal: A, Junction of upper 1/4 and lower 3/4 of spine of D7; B, just above spine of D9.
12th Dorsal: A, Junction of upper 1/4 and lower 3/4 of spine of D8; B, just below spine of D9.
1st Lumbar: A, Midway between spines of D8 and D9; B, lower border of spine of D10.
2nd Lumbar: A, Middle of spine of D9; B, junction of upper 1/3 and lower 2/3 of spine of D11.
3rd Lumbar: A, Middle of spine of D10; B, just below spine of D11.
4th Lumbar: A, Just below spine of D10; B, junction of upper 1/4 and lower 3/4 of spine of D12.
5th Lumbar: A, Junction of upper 1/3 and lower 2/3 of spine of D11; B, middle of spine of D12
1st Sacral: A, Just above lower border of spine of D11.
5th Sacral: B, Lower border of spine of L1.
Coccygeal: A, Lower border of spine of L1; B, just below upper border of spine of L2.
From Reid, R.W The relations between the superficial origins of the spinal nerves from the spinal cord and the spinous processes of the vertebrae. J. A. Physiol. 23:341-353, 1889.
Section Top | Title Page
Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.
All contents copyright © 1995-2024 the Author(s) and Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. All rights reserved.
"Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D.
Anatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. Advertising is not accepted.
Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not.
The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/