

Atlas of Human Anatomy in Cross Section: Section 4. Upper Limb
Ronald A. Bergman, Ph.D., Adel K. Afifi, M.D., Jean J. Jew, M.D., and Paul
C. Reimann, B.S.
Peer Review Status: Externally Peer Reviewed
|
Upper Left Quadrant |
Lower Left Quadrant |
Lower Right Quadrant |
Upper Right Quadrant |
|
1 . Cephalic v. |
6. Radial collateral a. |
8. Radial nerve |
13. Brachial a. |
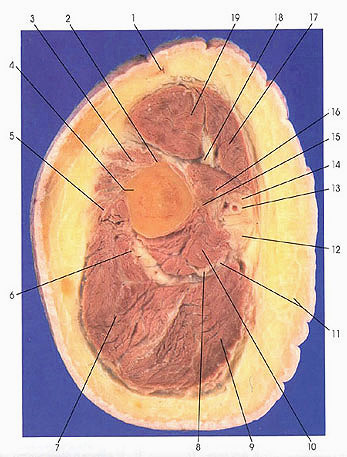
This section passes through the humerus at the distal end of the insertion of the deltoid muscle (3) onto the deltoid tuberosity (2) of the humerus. The deltoid makes its last appearance in this section.
The musculocutaneous nerve lies on the coracobrachialis muscle (16), which it pierced in its course through the upper arm.
The median nerve (14) lies above the brachial artery (13) and the ulnar nerve (12) below. The radial nerve (8) has migrated from its original medial position below (dorsal) the brachial artery (13) to one that is posterior to the humerus and between the medial head (10) and the long (9) and lateral (7) heads of triceps brachii. It continues its lateral migration in subsequent sections.
All of the muscular components of the anterior and posterior compartments are present in this section. The anterior compartment muscles include biceps brachii (17, 19), brachialis (5), and coracobrachialis (16). The posterior compartment muscle is triceps brachii (7, 9, 10).
The anterior compartment flexor muscles of the arm are innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve, and the large posterior compartment extensor muscle is innervated by the radial nerve.
Next Page | Previous Page | Section Top | Title Page
Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.
All contents copyright © 1995-2024 the Author(s) and Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. All rights reserved.
"Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D.
Anatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. Advertising is not accepted.
Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not.
The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/