

Atlas of Human Anatomy in Cross Section: Section 6. Pelvis, Perineum, Hip, and Upper Thigh
Ronald A. Bergman, Ph.D., Adel K. Afifi, M.D., Jean J. Jew, M.D., and Paul
C. Reimann, B.S.
Peer Review Status: Externally Peer Reviewed
|
Upper Left Quadrant |
Lower Left Quadrant |
Lower Right Quadrant |
Upper Right Quadrant |
|
1. Pyramidalis m. (first appearance) |
16. External iliac v. and obturator nerve |
28. fourth sacral canal and sacral intervertebral cartilage |
42. Obturator nerve |
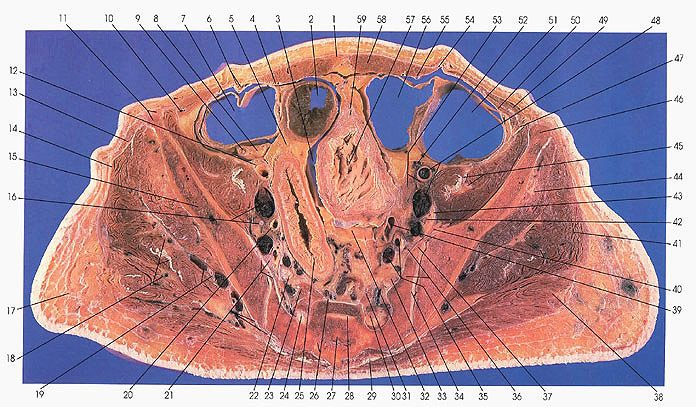
This section passes through the third sacral vertebra (27) and the anterior sacral foramina, in which the third sacral nerve (24, 30) is located. The fourth pair of sacral nerves (26) lie within the sacral canal (28) near the anterior sacral foramina. The sacroiliac joints (34) and the anterior superior spines (11, 46) of os ilium are seen in this cut.
On the right side, the bifurcation of the common iliac into the external and internal iliac veins (16, 20) is complete.
Piriformis (23, 31), tensor fasciae latae (13), and pyramidalis (1) muscles appear for the first time. Note an unusual (var.) origin of transversus abdominis (50) and internal oblique (49) muscles from the iliac fascia covering the iliacus (47) muscle.
The inguinal ligament (11) has its origin from the anterior superior spine (11).
The cecum (7), mesoappendix (8), and vermiform appendix (9) are seen in this section.
Next Page | Previous Page | Section Top | Title Page
Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.
All contents copyright © 1995-2024 the Author(s) and Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. All rights reserved.
"Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D.
Anatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. Advertising is not accepted.
Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not.
The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/