

Ronald A. Bergman, Ph.D., Adel K. Afifi, M.D., Paul M. Heidger,
Jr., Ph.D.
Peer Review Status: Externally Peer Reviewed
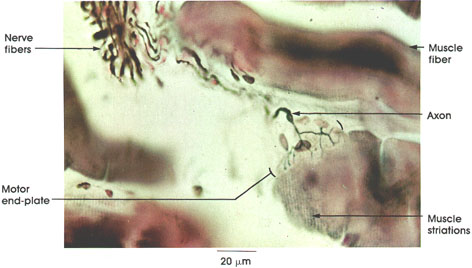
Rat, 10% formalin, Bodian silver, 612 x.
The tissue seen here was paraffin embedded and sectioned at 20 µm. This beautiful method permits a comprehensive view of the components of the nerve-muscle junction. The subneural region is seen to better advantage in Plate 117.
Nerve fibers: Myelinated somatic motor nerve fibers branch extensively within and between the muscle fibers. Axons (but not their myelin sheaths) are stained in this preparation.
Axon: Although not shown, nerve fibers lose their myelin sheaths as they approach the motor end plate region. These nonmyelinated axons branch extensively on the surface of the muscle fiber.
Motor end plate: A well-defined junction of axon terminals on the muscle fiber surface. It is at this place that the electrical nerve impulse is chemically (acetylcholine) transferred to the muscle fiber. A muscle action potential is generated, and the electrical impulse is conducted over the fiber surface, resulting in muscular contraction.
Muscle striations: Note that the striated myofibrils do not extend inside the motor end plate region.
Muscle fiber: The number of muscle fibers supplied by a single motor nerve fiber varies greatly. The ratio is low (about 1:3) for muscles that perform delicate functions, such as the extrinsic eye muscles. In limb muscles, the ratio may be 1:80 or greater.
Next Page | Previous Page | Section Top | Title Page
Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.
All contents copyright © 1995-2024 the Author(s) and Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. All rights reserved.
"Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D.
Anatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. Advertising is not accepted.
Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not.
The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/