

Ronald A. Bergman, Ph.D., Adel K. Afifi, M.D., Paul M. Heidger,
Jr., Ph.D.
Peer Review Status: Externally Peer Reviewed
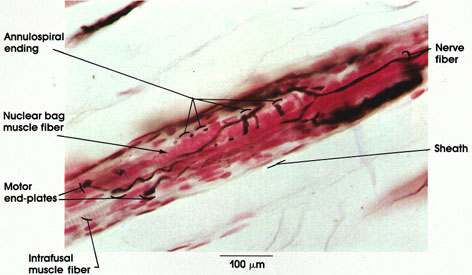
Cat, 20% formalin, Bielschowsky's method, 162 x.
Muscle spindles are found within skeletal muscles. Each spindle is formed of 2 to 10 small muscle fibers, the intrafusal fibers, enclosed within a sheath of connective tissue that is pierced by nerve fibers.
Nerve fibers: Leaving and entering the muscle spindle, they may carry the sensory signals (output) or the motor signals (input).
Sheath: Connective tissue capsule that surrounds the intrafusal muscle fibers of the spindle.
Annulospiral endings: Also known as primary or nuclear bag endings. Large axon with many branches and terminal enlargements. Arborization of this type of ending occurs around the nuclear bag variety of intrafusal muscle fibers. These endings have a low threshold to stretch. They discharge when the intrafusal muscle fibers are stretched. The receptors are silent when the extrafusal (ordinary) muscle fibers contract and the intrafusal fibers are relaxed. Central processes of the annulospiral endings in the spinal cord participate in the monosynaptic (myotatic) reflex.
Nuclear bag muscle fibers: Larger variety of intrafusal muscle fibers. They have an enlarged equatorial region to accommodate numerous small nuclei (Plate 121). It is here that annulospiral endings arborize.
Motor end plates: The smaller nerve fibers within the spindle are axons of gamma neurons in the spinal cord. The axons terminate as typical motor end plates on intrafusal muscle fibers.
Intrafusal muscle fibers: Small striated muscle fibers rich in sarcoplasm and arranged parallel to the extrafusal skeletal muscle fibers. Two to 10 fibers enclosed in a connective tissue capsule form the muscle spindle.
Next Page | Previous Page | Section Top | Title Page
Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.
All contents copyright © 1995-2024 the Author(s) and Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. All rights reserved.
"Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D.
Anatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. Advertising is not accepted.
Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not.
The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/