

Ronald A. Bergman, Ph.D., Adel K. Afifi, M.D., Paul M. Heidger,
Jr., Ph.D.
Peer Review Status: Externally Peer Reviewed
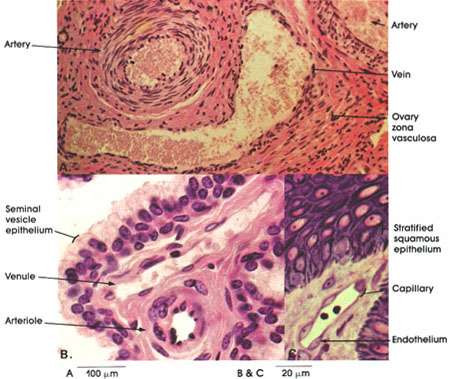
Human, 10% formalin, H. & E. A. 162 x., B. 612 x.
Human, glutaraldehyde-osmium fixation,
toluidine blue stain, C. 612 x.
This plate compares the histology of arteries, veins, and capillaries.
In A, a muscular artery and a vein from a human ovary are seen. Note, in the artery, the thick tunica media composed of many concentric layers of smooth muscle. The intima of such arteries is small and the adventitia is either equal to or smaller than the thick media. The internal and external elastic membranes between the intima-media and the media-adventitia are not seen in this type of preparation. Compare the predominantly muscular tunica media of muscular arteries with that seen in elastic arteries such as the aorta (Plate 152). The adjoining vein by contrast has a much thinner wall. Scattered smooth muscle fibers and fibroelastic connective tissue form this thin wall. Compare the sizes of the arterial and venous lumina.
In B, a venule and an arteriole are shown. Arterioles are not visible to the naked eye. Their walls are thick in comparison to the lumina. The tunica intima is thin and is composed almost exclusively of the endothelial lining. The tunica media is muscular and is the thickest coat. The tunica adventitia is smaller than the tunica media.
Note the pseudostratified epithelium of the seminal vesicle.
In C, a capillary is seen in a section of human skin. Note the extremely thin wall and the bulging endothelial cell nuclei. Capillaries are tiny enclothelial tubes between terminal arterioles and venules through which gases, nutrients, and metabolic wastes are transferred. The endothelium is continuous throughout the vascular system and heart.
Next Page | Previous Page | Section Top | Title Page
Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.
All contents copyright © 1995-2024 the Author(s) and Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. All rights reserved.
"Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D.
Anatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. Advertising is not accepted.
Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not.
The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/