

Ronald A. Bergman, Ph.D., Adel K. Afifi, M.D., Paul M. Heidger,
Jr., Ph.D.
Peer Review Status: Externally Peer Reviewed
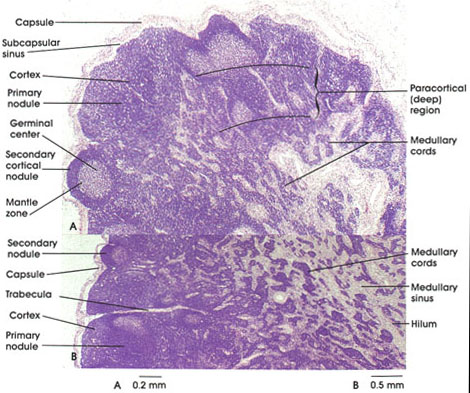
Human, 10% formalin, H. & E., A. 40 x; B. 25 x.
Lymph nodes are small encapsulated organs composed of a dense reticular meshwork ensheathed by stellate reticular cells and lymphoid tissue and cells. Nodes act as in-series filters for lymph carried in lymphatic vessels. Each node receives lymph from a limited region, but all lymph must pass through at least one lymph node. The course of lymph through a node begins in the (1) afferent lymphatic vessel, which perforates the capsule; lymph filters through the (2) subcapsular space to enter (3) peritrabecular and medullary sinuses where virtually all antigens and cellular debris are removed by macrophages suspended in the sinuses. The lymph exits via (4) efferent lymphatic vessels at the hilum of the node.
Lymph nodes have a cortex and a medulla.
The cortical region contains both primary and secondary nodules (follicles). Primary follicles differ from secondary follicles in that they do not possess germinal centers. It has been suggested that germinal centers are composed of immunoblasts (activated lymphocytes), which arise when an antigen is present. This results in mitoses of lymphocytes and their subsequent differentiation into plasma cells or small B lymphocyte memory cells. The memory B lymphocytes are ultimately located in the mantle zone of secondary follicles and are long-lived.
T lymphocytes are located in the paracortical zone of the node while the predominant remainder are B lymphocytes.
The medulla consists of medullary cords composed of packed lymphocytes and numerous plasma cells. Around the cords are medullary sinuses that join efferent lymphatic vessels that conduct lymph from the node.
Next Page | Previous Page | Section Top | Title Page
Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.
All contents copyright © 1995-2024 the Author(s) and Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. All rights reserved.
"Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D.
Anatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. Advertising is not accepted.
Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not.
The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/