

Ronald A. Bergman, Ph.D., Adel K. Afifi, M.D., Paul M. Heidger,
Jr., Ph.D.
Peer Review Status: Externally Peer Reviewed
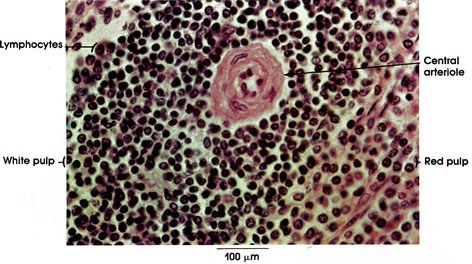
Rhesus monkey, Helly's fluid, H. & E., 162 x.
White pulp: Compact lymphatic tissue sheath surrounding the central arteriole. This sheath forms ovoid enlargements at intervals. The enlargements, known as lymphatic nodules, splenic nodules or Malpighian* corpuscles, may have germinal centers. Blends into the adjacent red pulp. Lymphocytes are the predominant cellular element, but plasma cells, macrophages, and other free cells are also found.
Red pulp: Less compact lymphatic tissue. Traversed by venous channels (sinusoids), imparting to it a reddish color in the fresh or unfixed state. Looks somewhat compact in fixed preparation because of the collapse of sinusoids.
Lymphocytes: Large, medium-sized, and small lymphocytes constitute the principal cell types found in the white pulp. They are compactly arranged in the white pulp and more loosely arranged in the red pulp.
Central arteriole: Courses in the white pulp. Adventitia is replaced by reticular tissue, which is infiltrated by lymphocytes in the white pulp. Supplies capillaries to the white pulp.
*Malpighi was a seventeenth-century Italian anatomist.
Next Page | Previous Page | Section Top | Title Page
Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.
Anatomy Atlases is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. 
"Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D.
Anatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. Advertising is not accepted.
Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not.
The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/