

Plate 10.185 Developing Tooth
Ronald A. Bergman, Ph.D., Adel K. Afifi, M.D., Paul M. Heidger,
Jr., Ph.D.
Peer Review Status: Externally Peer Reviewed
Kitten, 10% formalin, H. & E., 40 x.
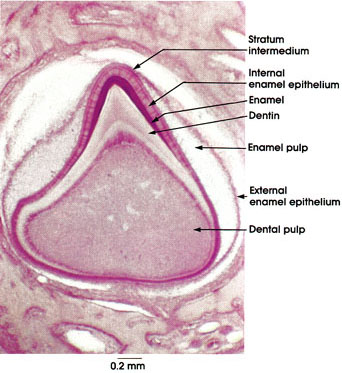
Internal enamel epithelium: A single layer of columnar cells. Cells here become the enamel-producing ameloblasts. A basement membrane separates the internal enamel epithelium from the dental pulp.
External enamel epithelium: A single layer of cuboidal epithelium.
Stratum intermedium: Two or more layers of cuboidal or squamous cells that separate the inner enamel epithelium from the stellate cells of the enamel pulp.
Enamel pulp: Or stellate reticulum, a collection of loosely arranged branching cells.
Enamel: Hardest substance in the body, composed of calcium salts in the form of apatite crystals and only 3 per cent organic material.
Dentin: Deposited by odontoblasts derived from dental pulp.
Dental pulp: Origin from dental papilla. Popularly but incorrectly called the nerve of the tooth.
Next Page | Previous Page | Section Top | Title Page
Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.
All contents copyright © 1995-2024 the Author(s) and Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. All rights reserved.
"Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D.
Anatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. Advertising is not accepted.
Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not.
The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/