

Plate 17.334 Pons
Ronald A. Bergman, Ph.D., Adel K. Afifi, M.D., Paul M. Heidger,
Jr., Ph.D.
Peer Review Status: Externally Peer Reviewed
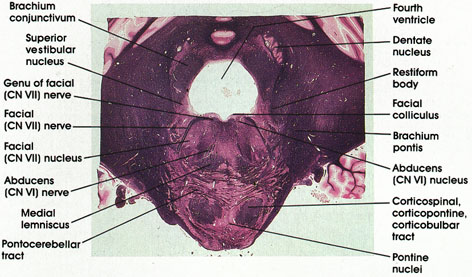
Human, 10% formalin, Pal-Weigert, 2.2 x.
Genu of facial (CN VII) nerve: A bundle of facial nerve fibers in the floor of the fourth ventricle.
Brachium conjunctivum: Also known as the superior cerebellar peduncle. Most important efferent fiber system of the deep cerebellar nuclei. Located clorsolateral to the fourth ventricle.
Superior vestibular nucleus: Located dorsal and medial to the restiform body. One of four vestibular nuclei. Receives fibers from the vestibular component of the vestibulocochlear (CN VIII) nerve and projects fibers to the cerebellum via the restiform body and to nuclei of extraocular movement via the medial longitudinal fasciculus.
Facial (CN VII) nerve: Coursing ventrolaterally to emerge at the lateral border of the pons.
Facial nucleus: Located medial to the facial nerve. Axons of neurons in the facial nucleus course medially and dorsally to reach the floor of the fourth ventricle (genu of facial nerve) before turning laterally and ventrally to exit from the lateral surface of the pons.
Abducens nerve: Rootlets of the abducens nerve are seen coursing in the tegmenturn of the pons. They arise from the medial aspect of the nucleus and exit from the ventral surface at the caudal border of the pons. Supply the lateral rectus muscle of the eye.
Medial lemniscus: Continuation of the same structure seen at more caudal and more rostral levels.
Pontocerebellar tract: Continuation of the same structure seen at more caudal levels. Axons of pontine nuclei destined for the cerebellum.
Pontine nuclei: Scattered between pontocerebellar fibers and the corticospinal, corticopontine, and corticobulbar fibers. Relay station between the cerebral cortex and cerebellum.
Corticospinal, corticopontine, corticobulbar tracts: Long descending fiber system originating in the cerebral cortex. Sectioned transversely as it passes through the basal portion of the pons.
Abducens nucleus: Located in a paramedian position in the floor of the fourth ventricle. Axons of neurons in this nucleus emerge from the medial aspect of the nucleus to form the abducens nerve. Lesions of the abducens nucleus result in ipsilateral paralysis of lateral gaze. The abducens nucleus and the adjacent genu of facial nerve together form the facial colliculus, a paramedian elevation in the floor of the fourth ventricle.
Brachium pontis: A massive bundle of fibers connecting the basal portion of the pons with the cerebellum. Also known as the middle cerebellar peduncle.
Restiform body: Continuation of the same structure seen at more caudal levels. Seen entering the cerebellum.
Dentate nucleus: The largest of the deep cerebellar nuclei. Axons of this nucleus are major components of the brachium conjunctivum.
Facial colliculus: A paramedian elevation in the floor of the fourth ventricle overlying the abducens nucleus and the genu of the facial nerve.
Next Page | Previous Page | Section Top | Title Page
Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.
All contents copyright © 1995-2025 the Author(s) and Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. All rights reserved.
"Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D.
Anatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. Advertising is not accepted.
Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not.
The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/