

Plate 17.347 Basal Ganglia
Ronald A. Bergman, Ph.D., Adel K. Afifi, M.D., Paul M. Heidger,
Jr., Ph.D.
Peer Review Status: Externally Peer Reviewed
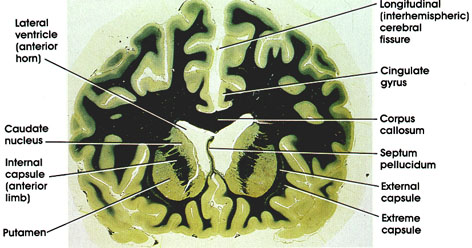
Human, 10% formalin, Weigert's hematoxylin (Loyez), 8 x.
Longitudinal (interhemispheric) cerebral fissure: Separates the two cerebral hemispheres. Filled with a dural fold, the falx cerebri, which has been stripped away in this preparation.
Cingulate gyrus: Located dorsal to the corpus callosum. A component of the limbic lobe, which, in addition to the cingulate gyrus, includes the subcallosal gyrus, isthmus, parahippocampal gyrus, and uncus.
Corpus callosum: A massive myelinated fiber bundle connecting the two hemispheres. important in interhemispheric transfer of information.
Septum pellucidum: A thin septum, ventral to the corpus callosum, separates the two lateral ventricles. May contain a cavity, the cavurn septi pellucidi.
External capsule: One of the efferent cortical bundles. The others include the internal and extreme capsules. Located lateral to the putamen.
Extreme capsule: One of the efferent cortical bundles. Lateral to the external capsule. Between the external and extreme capsules is the claustrum (not seen in this preparation).
Lateral ventricle: Anterior horn of the lateral ventricle. Note the characteristic bulging of the head of the caudate nucleus into the cavity of the ventricle.
Caudate nucleus: C-shaped mass of gray matter closely related to the lateral ventricle. The part seen in this figure is the head of the caudate, which has a characteristic bulge into the lateral ventricle. This characteristic bulge is lost in the disease Huntington's chorea. The caudate nucleus is part of the basal ganglia, and thus plays a role in the regulation of movement. Huntington was a nineteenth-century American physician.
Internal capsule: Heavily myelinated broad band of white substance that arises from wide areas of the cerebral cortex and descends to the brain stem and spinal cord. Carries fibers from and to the cerebral cortex. The anterior limb of the internal capsule separates the caudate nucleus and putamen.
Putamen: Located lateral to the anterior limb of the internal capsule and medial to the external capsule. The putamen, like the caudate, is a component of the basal ganglia and thus plays a role in motor control.
Next Page | Previous Page | Section Top | Title Page
Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.
All contents copyright © 1995-2024 the Author(s) and Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. All rights reserved.
"Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D.
Anatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. Advertising is not accepted.
Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not.
The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/