

Relaxed and contracted muscle fibers
Ronald A. Bergman, Ph.D., Adel K. Afifi, M.D., Paul M. Heidger,
Jr., Ph.D.
Peer Review Status: Externally Peer Reviewed
Human; Helly's fluid;
A., C., phosphotungstic acid hematoxylin,
B. Mallory-azan,
D. H. & E.; 4416 x.
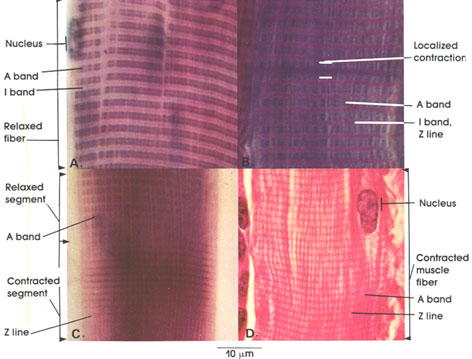
In this plate, the structural basis of skeletal muscle fiber contraction is shown.
A: Relaxed fiber showing distinct cross striations, the darker staining A band and the lighter staining I band. Note that the I band is bisected by a thin but deeply staining line (Z line), while the A band is bisected by a lightly staining line (H zone).
B: A fiber seen in the relaxed state except for a small segment of localized contraction. Note the change in the band pattern in this segment. Two adjacent A bands are in contact, and the I band has disappeared.
C: A fiber shown with both a relaxed and contracted segment. The A and I bands are clearly outlined in the relaxed segment but not in the contracted segment. In contraction, the I band becomes narrower and disappears. The A band does not normally become shorter except in extreme contraction. Contraction bands appear as a result of an increase in density and staining of the Z line.
D: A portion of a fully contracted muscle fiber is shown. The changes here are similar to those described in C for a contracted segment except that the normal distance between the thickened Z lines (contraction bands) is reduced, denoting extreme contraction.
Next Page | Previous Page | Section Top | Title Page
Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.
All contents copyright © 1995-2024 the Author(s) and Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. All rights reserved.
"Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D.
Anatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. Advertising is not accepted.
Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not.
The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/